One Sample Poisson Rate Help
Home » SPC for Excel Help » Statistical Tools » Sample Tests Help » One Sample Poisson Rate Help
The One Sample Poisson Rate technique is used to estimate the population rate of a Poisson distribution. That estimate is then compared to a target value to determine if the estimated rate is different from the target value or not. A confidence interval can be calculated to define a range of values that are likely to contain the rate. This interval can be one or two sided.
The example below demonstrates how to do this test. You can download the data at this link.
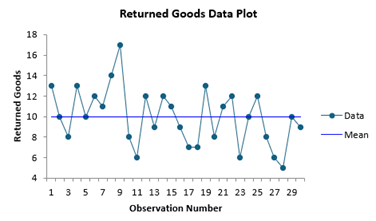
A customer service manager has been returning the number of returned goods per day. He wants to know if the rate of returned goods is 10 returned goods per day. He has collected data on the number of returned goods per day for 30 days. The steps to perform the analysis are given below.
1. Enter the data into a worksheet as shown below. The data must be in one column.
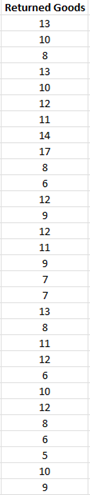
2. Select the data above (including the heading).
3. Select “Poisson Rate Tests” from the “Statistical Tools” panel in the SPC for Excel ribbon.
4. Select the “One Sample Poisson Rate.” The input form below is shown.
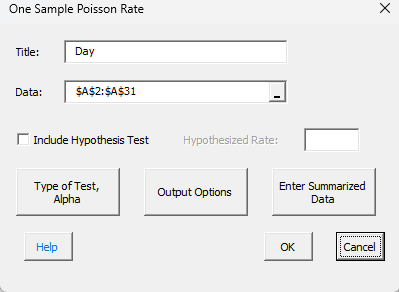
- Title: Name of variable or test, default is first cell in range selected if it is non-numeric.
- Data: This is the worksheet range containing the data; the default is the selected worksheet range, less the first cells if it is non-numeric.
- Hypothesized Rate: If the “Include Hypothesis Test” option is selected, the hypothesized rate is enabled; enter the hypothesized rate.
- Type of Test, Alpha: The input form below is shown if this option is selected.
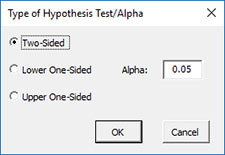
- Select the Type of Test: two-sided; lower one-sided, or upper one-sided, the default is two-sided.
- Alpha: this is the confidence level; 1-alpha is the confidence interval; default is 0.05 or 95% confidence interval.
- Output Options: the input form below is displayed if this option is selected.
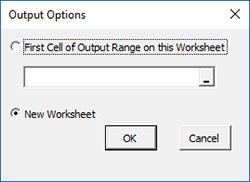
- First Cell of Output Range on this Worksheet: Select this option if you want the output on an existing worksheet; then select the first cell of the range where you want the output placed; a check is made to ensure that no existing data are overwritten in the worksheet.
- New Worksheet: Select this option if you want the results on a new worksheet.
- Enter Summarized Data: the input form below is displayed if this option is selected.
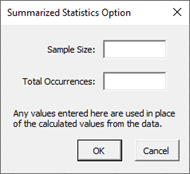
- You may enter the sample size and total occurrences; any value that is entered will be used in place of the values calculated from the data.
- Select OK or Cancel to return to first input form above.
One Sample Poisson Rate Output
The output from the one sample Poisson rate technique is shown below. In this example, the hypothesized rate is 10. It is a two-side hypothesis test with alpha = 0.05.
An explanation of terms is given below the output. In addition to the output table, the program displays two charts to help interpret the results.
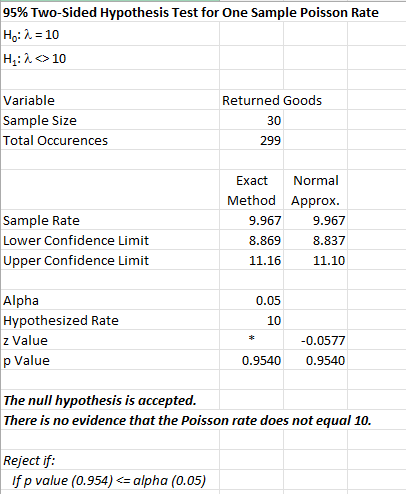
The output tells you the conclusion from the test. The null hypothesis (H0) and the alternate hypothesis (H1) are printed below the title.
- Variable: Name of variable
- Sample Size: Number of data points
- Total Occurrences: Number of occurrences in the samples
- Sample Rate: average number of occurrences per length of observation in the sample
- Lower Confidence Limit: the calculated lower confidence limit
- Upper Confidence Limit: the calculated upper confidence limit
- Alpha: Value of alpha entered by user (default is 0.05)
- Hypothesized Rate: entered by the user, hypothesized sample rate
- p-Value: calculated p-value; in red if p-value < alpha; probability of obtaining the sample rate above if the null hypothesis is true.
- The bold output gives the conclusion if the null hypothesis is accepted or not. In this example, since p is greater than alpha, there is no evidence that the Poisson rate is not equal to the hypothesized rate.
- The criteria to reject the null hypothesis is also given.
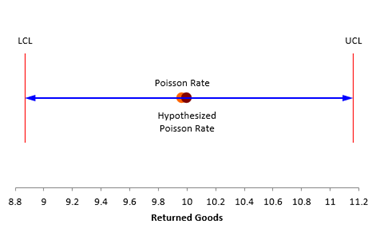
The chart below is also created. This makes it easy to see if the hypothesized rate is within the confidence interval or how far away it is from the confidence interval.
There is also a chart of the data to look for possible outliers. If the program detects possible outliers, they will be in red and a message will be printed on the worksheet.